





Disc pelletizer, also known as pan granulator and balling disc machine, is developed from newly improved granulation equipment based on traditional equipment structure combined with practice. The equipment has the characteristics of uniform pellet size, low water content, high strength, simple structure, convenient control and stable operation.
The inclination and rotation speed of the discs for pelletizing and discharging can be changed to improve the pelletizing efficiency.
The raw powder flows into the disc from the feeding pipe, meanwhile the water spray pipe located below the feeding pipe sprays water on the powder. Due to the wetting and adhesion of water droplets, many small balls are formed with each drop of water as the core. Under the action of gravity and centrifugal force, the ball rolls downward, and the powder adheres along the way to make the ball grow gradually, at the same time, the ball rotates with the friction force of the disc.
When the balls rotate to the scraper plate, due to the small gap between the scraper plate and the bottom of the disc, only unballed powder can pass through, while most of the balls are scooped up by the scraper plate and flow down the scraper plate. Along the way, the powder is again bonded and rolled towards the edge of the plate, and in this way, the small balls gradually grow up. When the required particle size is reached, due to the mass effect of the small balls and the smooth surface after pelletizing, the friction with the bottom of the disc is not enough to rotate with the disk. It can only be rolled in the discharge area, and when it accumulates to a certain height, it is scraped out by the scraper plate.
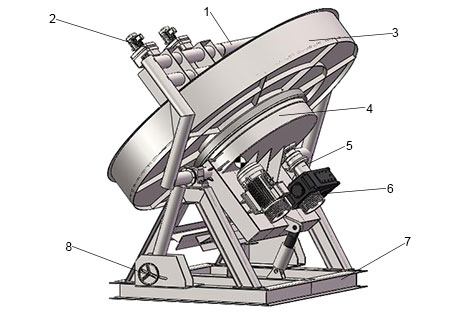
1. low/Scraper holder 2. Plow/Scraper 3. Pan/Disc 4. Bevel gear 5. Main shaft 6. Transmission 7. Structure steel base 8. Angle adjustment
High wear-resistant liner, reducing the adhesion and wear of the disk surface, easy to replace and disassemble.
High deformation resistance and high flatness.
The main shaft and bearing are quick-release structure, double-channel oil seal, reliable and convenient to use.
High surface hardness scraper with surface welding. Pretty long service life.
Motor—reducer—pinion gear—big gear.
Semi-enclosed or fully enclosed structure. The semi-enclosed structure has a unique sealed and dustproof structure. Fully enclosed structure can greatly improve the gear lubrication environment and extend its service life.




| Model | Disc diameter (m) | Disc depth (m) | Rotating speed (rpm) | Scrap type | Capacity (t/h) | Power (kW) |
| QP20 | 2 | 0.4 | 15.1 | fixed | 7.2(cement) | 15 |
| QP25 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 12.5 | fixed | 11(cement) | 15 |
| QP28 | 2.8 | 0.4-0.5 | 11.8 | fixed | 6.5-9.5(metallurgy) 14(cement) | 18.5 |
| QP32 | 3.2 | 0.45-0.65 | 11 | fixed | 8-12(metallurgy) 18.5(cement) | 22 |
| QP35 | 3.5 | 0.45-0.65 | 10.5 | fixed | 9.5-14.5(metallurgy) 22(cement) | 30 |
| QP40 | 4 | 0.5-0.8 | 8.6-11 | fixed | 12.5-19(metallurgy) 29(cement) | 45 |
| QP45 | 4.5 | 0.5-0.8 | 8.1-10 | rotating | 16-24(metallurgy) 36.5(cement) | 55 |
| QP50 | 5 | 0.6 | 6.8-8.2 | rotating | 20-30(metallurgy) | 75 |
| QP55 | 5.5 | 0.6-0.7 | 6.6-8 | rotating | 24-36(metallurgy) | 90 |
| QP60 | 6 | 0.6-0.7 | 6.2-7.6 | rotating | 29-43(metallurgy) | 110 |
| QP70 | 7 | 0.7 | 4-5 | rotating | 35-52(metallurgy) | 160 |






What is Cyanuric Acid and Its Applications Cyanuric acid (CYA) is an…

What is Potassium Sulfate and Why Granulate It Potassium sulfate, commonly referred…

With the rise of precision agriculture and crop-specific nutrient strategies, specialty compound…

In briquetting, the binder is often the unsung hero. Whether you’re compacting…

Mixing and pelletizing processes are very important steps in the sintering production…

The Main Source of Ammonium Chloride The combined Alkali process (Hou’s process)…