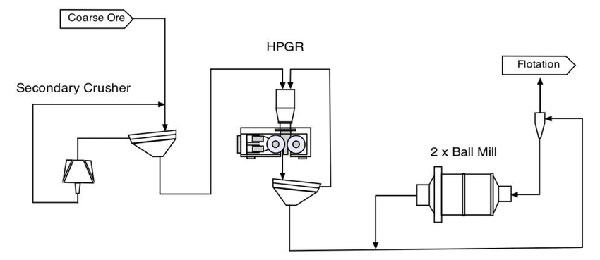
HPGR and ball mill are both widely used ore crushing (grinding) equipment. Within comminution circuits, High Pressure Grinding Rolls (HPGR) are increasingly replacing ball mills for hard rock reduction – owing to their substantially lower energy consumption and potential for significant total cost of ownership reduction.
but these two machines differ in working principle, structural characteristics, and application scope.
Working Theory
HPGR
HPGR generates strong pressure through clamping and shearing forces, crushing materials between two rotating rollers. In practical production, controlling the roller gap and working pressure adjusts the material’s dwell time and degree of crushing between the rollers. With multiple forces applied and repeated crushing during the process, the crushed particles have uniform size and large specific surface area, enhancing material reactivity and mechanical strength.
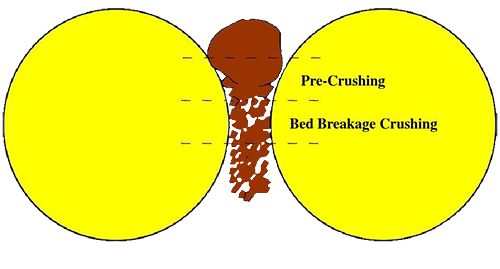
It is quasi-static pressure crushing, compared to impact crushing, saves about 30% energy by implementing layer-by-layer crushing of materials, facilitating mutual grinding between particles.
Ball Mill
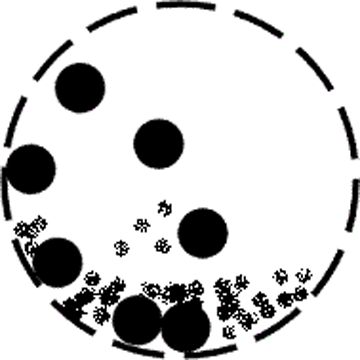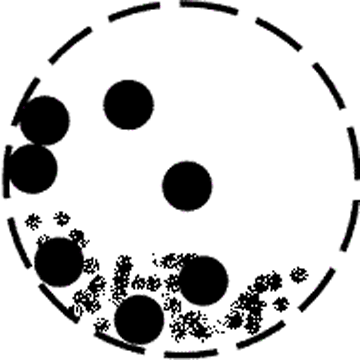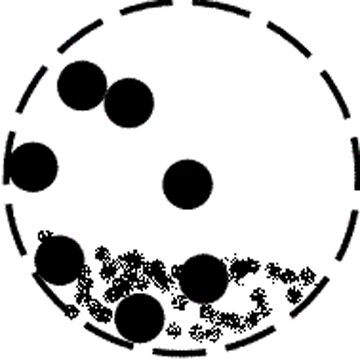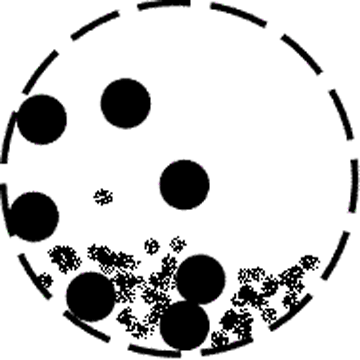
In a ball mill, a certain amount of steel balls (or balls with any suitable material) are added to the grinding dish. Friction and collisions generated by the gravity of the balls and the rotation of the dish crush the materials. Compared to the roller press, the ball mill has fewer crushing cycles and lower efficiency. However, it better preserves the physical and chemical properties of the raw materials, especially for harder materials, resulting in superior grinding effects.
Structure
HPGR
The main components of HPGR are the rollers and the frame. The gap between two rollers and the pressure used can vary, and can be adjusted according to the desired degree of material crushing for optimal process efficiency. Additionally, HPGR is known for its advantages of simple structure, ease of use, and energy-saving.
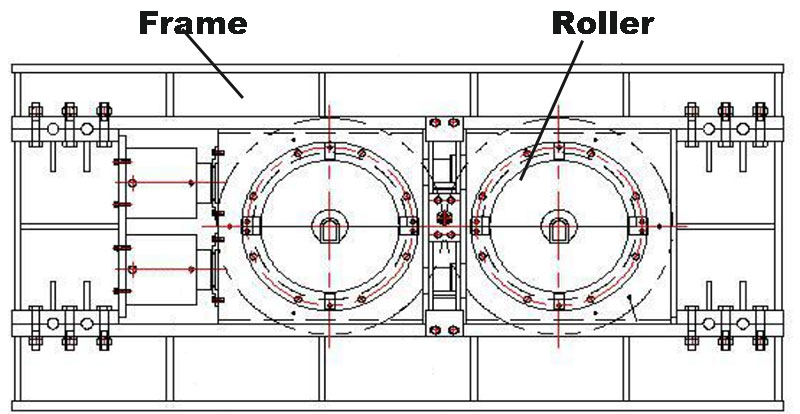
Ball Mill
A ball mill consists of rotating and fixed parts. The rotating part comprises the grinding drum and grinding balls, typically installed horizontally. The combined action of the grinding drum and balls increases production efficiency and results in finer material grinding.
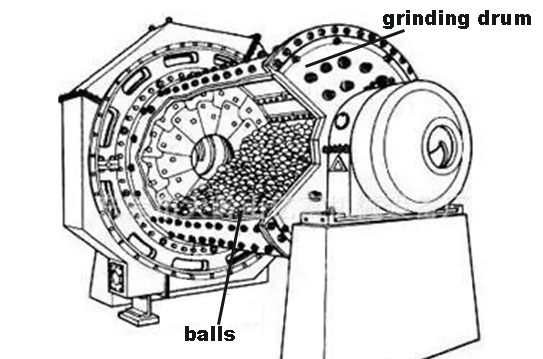
Application
HPGR
HPGR is widely utilized in the cement industry for grinding, in the chemical industry for pelletizing, and for fine grinding to increase the specific surface area of pelletized ore in pelletizing plants. HPGR can deal with raw material with a bit high moisture, but very high moisture material is not accepted.
It is employed in the crushing of metal ores to simplify the ore crushing process, reduce the amount of grinding, enhance system production capacity, improve grinding efficiency, or achieve different production objectives such as beneficiation indicators.

Ball Mill
Ball mills can be divided into two types: dry grinding and wet grinding. It is suitable for grinding materials with high hardness, particularly some metal ores. However, due to issues such as grinding ball wear, achieving the desired fineness of material in ball mills can sometimes be challenging.
It is now the key equipment where materials are crushed before undergoing further grinding.
Although HPGR (high pressure grinding roll) is associated with grinding, in cases where high grinding precision is required, additional grinders like ball mills are paired later in the process. Ball mills are a more traditional option for this purpose. Considering the energy efficiency of the entire powder grinding production line, we should adhere to the principle of “more crushing and less grinding.” It’s essential to select suitable crushing methods and equipment based on the characteristics of different materials, thereby optimizing the configuration of production line equipment.