What is lime
Lime, also known as quicklime or burnt lime, is mainly composed of calcium oxide, molecular formula CaO, which is a white block or powder cubic crystal. The lime commonly used in industry will be dark gray due to impurities such as magnesium oxide, aluminum oxide and ferric oxide. The relative density is 3.25-3.38g/cm3, the true density is 3.34g/cm3, and the bulk density is 0.8-1.2g/cm3. Its melting point is 2614 Celsius, boiling point is 2850 Celsius, soluble in acid, unstable in the air, and will react with water and carbon dioxide in the air to form calcium hydroxide and calcium carbonate.
History of lime
Quicklime manufacturing is an ancient industry with a long history. Humans began to produce quicklime thousands of years ago. After the limestone is calcined, quicklime and hydrated lime appear. Quicklime is used to make mortar, and hydrated lime is used for coloring, painting, and whitewashing. Lime was used in the construction of the pyramids in Egypt, the Great Wall of China, and the construction of Roman aqueducts. Humans first produced lime intermittently by laying stones or digging pits and laying stones, and this method has been used until now.
In the 18th century, people began to use flare kilns to continuously produce lime, and in the 19th century, rotary kilns and wheel kilns for firing pottery products were used to burn lime. In 1865, the “German Association for Clay Bricks, Clay Products, Lime and Cement” was established in Berlin. In the middle of the 19th century, the lime industry in Europe developed. After the Second World War, mechanized shaft kilns entered the lime manufacturing industry, and the lime industry was able to improve technology, increase production efficiency, and improve services.
By 1977, the lime sold in the United States was classified according to its usage: metallurgy and chemical industry, construction, agriculture, calcined dolomite, etc.
In 1980, the Soviet Union’s lime production was 30 million tons. The largest lime producers are concentrated in ferrous metallurgical and chemical complexes.

How lime is produced – making lime from limestone
Lime is produced by decomposing calcium carbonate at temperatures around 900-1100 Celsius. Calcium carbonate is calcined to produce lime and generate carbon dioxide. The ores rich in calcium carbonate mainly include limestone, dolomite, and chalk, etc.
Furnaces used for calcined calcium carbonate are mainly shaft kilns and rotary kilns. In addition, there are CID kiln, suspension kiln, etc.
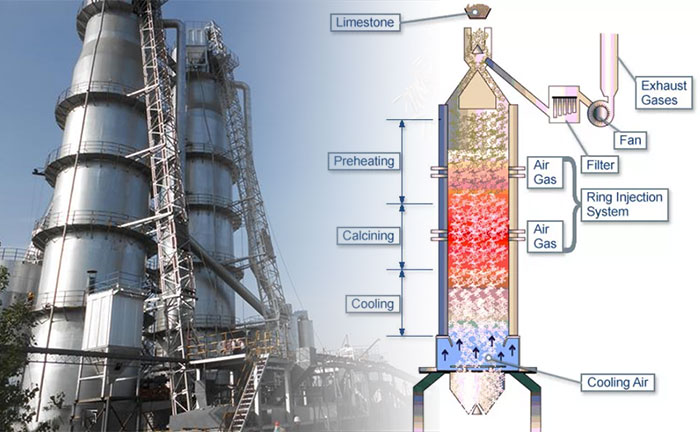
How lime is produced in shaft kilns
The shaft kiln is with a cylindrical kiln body. Materials are fed from the top of the kiln and discharged from the bottom of the kiln after calcination.
Materials in the shaft kiln go through preheating zone, calcining zone and cooling zone.
In the preheating zone, the material is preheated with the help of the heat of the flue gas. In the calcination zone, the material is sintered with the help of the heat released by the fuel combustion. In the cooling zone, the calcined material exchanges heat with the blowing cold air , itself is cooled, and the air is heated and enters the dry burning zone as combustion air.
In order to ensure that all stages of the material firing process are carried out fully and completely, the three belts in the shaft kiln should maintain a certain height and strive to be stable.
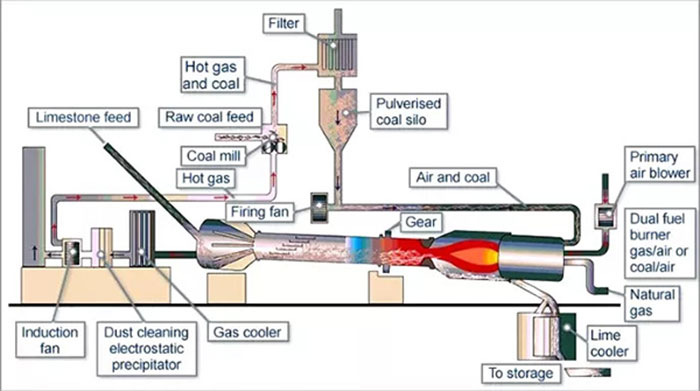
How lime is produced in a rotary kiln
The rotary kiln has a high end and a low kiln head, with a slope of about 3%. It rotates at a speed of 1-3 rpm. The material enters from the preheater through the kiln end, and is discharged from the kiln head to the cooler. Limestone is decomposed by heat during the movement from the kiln end to the kiln head. The kiln head is equipped with a burner to supply heat to the kiln.
The flue gas produced by combustion flows from the kiln head to the kiln end under the action of negative pressure at the kiln end, and is discharged from the kiln end.
The material and the flue gas move in reverse, firstly preheated by the preheater, and then the raw material is evenly fed into the kiln from the kiln end. During the rotation of the kiln body, the material moves from the kiln tail to the kiln head, and is discharged from the kiln head to the outside of the kiln and enters the cooler for cooling.
The coolers matched with the rotary kiln include vertical coolers, pushing coolers, single-tube and multi-tube coolers, etc. The temperature of lime falling into the cooler is about 1100°C, and the temperature out of the cooler is less than 100°C.
Lime in the metallurgy – why lime is added in smelting process
Lime is main in the metallurgy in 3 areas
1. Iron production
Lime is widely used as a slagging material in the blast furnace ironmaking process.
CaO in blast furnace slag comes from sinter or added lime and dolomite. Lime production branches usually do not supply lime directly to blast furnaces. About half of the limestone mines in iron and steel plants are indirectly (via sinter) supplied to blast furnace ironmaking. This is because the amount of iron slag in blast furnace ironmaking is much larger than that in steelmaking.
2. Iron melt pretreatment
In iron melt pretreatment, lime is mainly used for desulfurization.
In the desulfurization of iron melt, lime is desulfurized after being industrially produced and processed by physical or chemical methods in the form of a composite desulfurizer.
3. Steel production
The purpose of steelmaking is mainly to remove various impurities in iron melt, like carbon, phosphorus, sulfur, etc. However, sulfur and phosphorus have a great influence on the quality of steel. To remove S and P is one of the main tasks of steelmaking.
Lime is widely used in the steelmaking process as a material for slagging and effective removal of S and P in the steelmaking process.
Lime briquette machine
During the production process of lime plant, a lot of dust will be generated. If the dust is not utilized, it will cause waste, and it will also cause environmental pollution due to transshipment and other situations. The briquetting machine is such a machine that can turn the dust into lime briquette for reuse.
Lime briquette machine mainly refers to the roll briquette machine. Put the lime that needs to be briquetted into the briquette machine, and after briquetting, the lime fine and dust can be pressed into various shapes of briquettes.
When the equipment is running, the dry lime is fed from the top of the equipment, and the material is forcibly exhausted by the screw pre-pressing device. Then enters two horizontal pressing rollers, and the two rollers are powered by the reducer to rotate at the same speed in opposite directions. Meanwhile, the material is forced to be fed between the two rollers. Adjust the screw shaft rotation speed to ensure that the upper space of the two rollers is always filled with materials.
The pocket on the surface of the rollers is in the state of opening its mouth to bite into the material. With the rotation of the roller, the pocket enters the closed state to compress the material (also known as re-exhaust), and then the pocket is in the state of opening again, and is compressed into a briquette. At this time, the briquette will naturally come out of the pocket due to the unbalanced force, the elasticity of the briquette and the action of gravity. During the briquetting process, the density of the lime can be increased by 1 to 3 times, so as to achieve the strength required.

Lime briquetting process
Lime briquetting is a binder free briquetting process, that is, a process that does not need to add any other additives. In the briquetting process, the quantitative feeding of the lime briquette machine is very important, so it is often set up a quantitative feeding device in the previous step of the briquette machine. After briquetting, due to the existence of small particles in the briquettes, it is very necessary to screen, so the produced briquettes often have to pass through a screening device, It can be simple, such as a fixed sieve, or a type of screening machine driven by motor.
The screened materials need to be re-introduced into the whole system for briquetting again. This whole set of system constitutes the briquetting process of lime.
The finished lime briquettes can be stored in the steel mill for several days for use, but long-term storage will cause the quality of the briquette to decline and the briquettes to disintegrate.
In addition to providing a complete set of briquetting processes, Maxton can also provide various types of equipment customized according to customer needs, feeding and discharging systems, and docking with on-site raw material systems as well as dust removal systems, or a complete set of EPC systems and corresponding solutions.
Raw material sources and system design considerations
In actual lime plants, not all lime fines are the same. Some come from dust collection systems, while others are screening fines separated during grading. These materials differ in particle size distribution and physical properties, which may influence the briquetting behavior.
Therefore, designing a complete system from feeding to briquetting and discharging is very important. Such a system ensures consistent performance, efficient recycling of all fines, and stable product quality.
Lime, a binder?
In the process of agglomeration and granulation, lime is used as a binder in the agglomeration of many raw materials, but due to the reaction between lime and water, quicklime cannot be used directly as a binder, or the finished pellet or briquette will face the same situation with pure lime briquettes.
In this case, the lime needs to be chemically reacted with water before it can be used to generate hydrarated lime for the agglomeration process. Therefore, what is actually used as a binder is hydrarated lime instead of quicklime.
Price of a lime briquette system
There are not many equipments in the lime briquetting system. A simple process only includes feeding equipment and lime briquetting machine. However, according to customer’s requirements, operating habits and raw material conditions, the configuration of various equipment can be very different. Therefore, the specific price depends on many aspects. Only when you really understand the demand can you find out the corresponding price.
The profit of lime briquetting
The value brought by the lime briquetting production line is very high. Taking a 300 ton/day lime kiln as an example, under relatively normal management, the dust generated per day is about 40 tons.
Before there is no briquetting, the market price of these dust is only $10 per ton (price depends on the local market). The overall cost of producing 1 ton of lime briquettes with a briquetting machine is about $20 (depends on many factors), and the market price after pressing into lime briquettes is as high as $100 per ton. And the lime briquettes made of pressed dust have higher purity, no burning phenomenon, and better activity.
We can roughly calculate the benefit, compared with the non-pressing production process, the daily value created by the briquetting ball production process is 40*(100-20-10)=$2800*365=$1,022,000. The profit per year would be about 1m USD!
Lime briquette machine manufacturer and system designer
Maxton is a professional manufacturer of lime briquetting machines. The machines are built with high-quality materials, long service life of wear parts, stable operation and low energy consumption, suitable for heavy-duty, long-term production.
The lime briquette machine from Maxton adopts a proven and mature mechanical structure, capable of handling higher pressures with stable performance. This design not only ensures stronger briquettes, but also reduces operating costs for customers by minimizing energy consumption and material loss.

In addition, the robust structure lowers the frequency of shutdowns and maintenance, allowing smoother operation and longer continuous production cycles. These advantages help customers achieve reliable performance, higher productivity, and lower overall costs.
Beyond equipment supply, Maxton provides professional process design services, ensuring that the lime briquetting system is well integrated with other on-site systems. This allows us to deliver optimized and reliable solutions that create maximum value for customers.






