







The kneader reactor has a fully enclosed unit that can be operated continuously, which can directly remove volatile matter, reduce energy and water consumption, and can be operated under vacuum or high pressure according to the characteristics of the solvent, so as to achieve better mixing and kneading characteristics, achieve more effective self-cleaning and more efficient surface renewal purposes. It is an ideal equipment for high viscosity material.
According to specific needs, it can be a double shaft device or a single shaft device. Batch type is also available.
A process includes polymerization, reaction, drying and evaporation, crystallization, dissolution.
The material is in the state of full mixed flow in the radial direction, and the characteristic of plug flow in the axial direction. The paddle is composed of blades and kneading rods. The two rotating shafts rotate in the same direction or in opposite directions, high-torque shafts are designed to realize this. The rotational speed of the rotating shaft is inversely proportional to the number of kneading rods.
There are kneading elements on the two rotating shafts of the reactor. During the rotation, the mutual meshing action between the paddles and the scraping between the paddles and the shell realize the efficient self-cleaning characteristics of the equipment and reduce the possibility of material accumulation and degradation is eliminated, the material can obtain rapid surface renewal. It also has efficient mixing characteristics.
The speed difference between the paddles intensifies the mixing process of the materials on the left and right sides. The middle area of the two paddles has a high shear rate and a large mixing index, so it has excellent distribution mixing and dispersion mixing performance.
The reactor also has a large effective reaction volume and axial transport capability.
 Raw material
Raw material 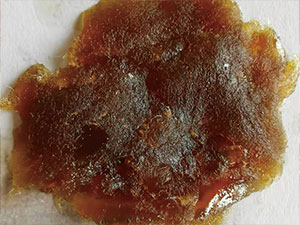 During kneading reaction
During kneading reaction  During kneading reaction
During kneading reaction 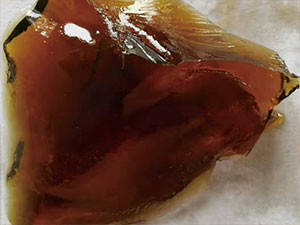 Output from kneader reactor
Output from kneader reactor The dissolution, reaction, evaporation concentration or drying of materials under vacuum or normal pressure is a common industrial process, usually encountered in the chemical, polymer, electronics, pharmaceutical, textile and other industries. If it is a high-viscosity material such as a paste, accompanied by foaming or scaling, it is difficult to achieve normal operation. In addition to the application of the single-shaft self-cleaning mixer, the double-shaft self-cleaning mixer is more competent for materials with high viscosity.
Dissolution and polymerization are conventional routes for elastomer material processing. In the process of polymer production, the solvent and emulsifier that form the polymer must be separated. This usually involves several steps including coagulation, exfoliation, various mechanical separation and drying stages, each of which is energy intensive, resulting in a significant amount of solvent being burned off in the waste steam, which requires specialized equipment and is more promising scheme to reduce aggregation steps.
Free lab test is aviliable now!
Filling ratio: 60-80%.
Material residence time: a few minutes to two hours.
Standard operating pressure: -0.1-0.05MPa, under special circumstances the pressure can up to 0.6MPa.
Operating temperature: 0-300°C.
Volume: 100L to 10000L.
Power: (11-320) kW.






Producing high-quality dry powder fire extinguishing agents requires not only the right…

Energy demand continues to grow worldwide, and industries are under increasing pressure…
Why Using Intensive Mixer in Sintering System The sintering production process primarily…

Mixing and pelletizing processes are very important steps in the sintering production…

With the intensification of the energy crisis, coal prices have risen sharply. At…