





The roller compactor or dry granulator is used for compaction which is the process of compressing fine-grained solids between two counter-rotating smooth or profiled rollers, it is much similar to the mechanism housed in our roller briquette machine. During the process, the material is turned into a kind of briquette called “flake”, which is an intermediate product. The final granular we would like to get will pass the crushing and screening processes to get the required size range.
MAXTON supplies spare parts for roller compactors, including rollers, screws, and more, ensuring comprehensive support for your maintenance needs.
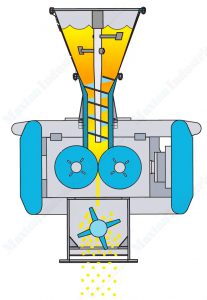
The material passes through the buffer bin, and then goes past the feeder, quantitatively and evenly enters the feed port of the roll briquette machine. After that, it reaches the pre-compression feeding device of the machine.
To maintain a stable material level in the pre-compression feeding device, the screw in the pre-compression feeding device will force the material into the middle of the rolls. The screw will pre-compress the material and remove the gas as much as possible from particles, and moves the material to be transported to the middle of two rolls.
At the arc-shaped notch of the rollers, the pockets of the same shape are evenly distributed on the surface of the two rolls or use even smooth rollers. Through the meshing transmission of the synchronous gear reducer, the two rollers run at the same speed and opposite to each other, thus the material will be transported to the arc-shaped notch. The material is bitten into the groove and forced to compress. As the rolls continue to rotate, when they exceed the center line, the finished flake will fall out of the pocket under the action of its own elasticity and gravity.
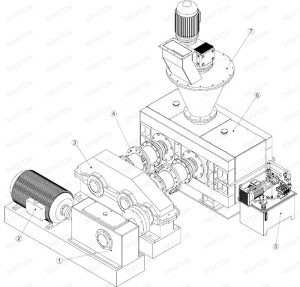
1. Angle reducer 2. Main motor 3. Main gearbox 4. Coupling 5. Hydraulic station 6. Main frame 7. Screw feeding
Motor——V belt, reducer or direct——Double shaft output reducer——Coupling——Rolls
Screw, double screws, more screws feeding or gravity feeding. Specially designed sealing structure.
Surface is cold worked, beams are connected by high-strength bolts.
Central lubrication or point lubrication.
Compaction is a process a bit different from briquetting which will include the next steps of crushing and screening.
The powdery material is pre-compressed and degassed by the screw feeder, and is quantitatively and evenly added between the two rollers of the compactor. After being squeezed between the rollers, the pressed material falls off from the pocket under the action of elasticity and gravity, forming a dense, hard strip of flake or briquette. During the compaction process, the pressure on the material gradually increases, when the gap between the two shafts is at the smallest position, the pressure on the material is maximum, and then gradually decreases until it reaches 0. The apparent density of the material can increase by 1.5 to 3 times on compaction.
The crushing work will be carried out by the flake breaker under the roller compactor, where the flakes are pre-broken or broken into small granules. Thin granules are easier to transport and are easily further broken by subsequent crushers when needed.
In the crushing process, the softer parts of the flakes are broken into high-strength and wear-resistant particles. These products will not be ground during transportation and use.
The crushed granules are divided into oversized granules, product granules and fine granules on a multi-stage screen. The fine granules on the lowest screen are recycled into the compactor and then compacted again. The oversized particles retained in the upper layer of the multi-stage screen need to be further crushed. After crushing it returns to screening.
Proper selection of crushing and screening equipment is crucial to the economy of the compacting system. The shape of the granules, the size range of the granules (typically 1 to 5 mm or 2 to 4 mm), and the amount of circulation after crushing and screening determine the output and capacity of the compacting system.
Feeding, handling, mixing, polishing, coating, packing, dust collecting, etc.

Roll Diameter: 220-1400mm
Capacity: 5 kg/ hour to 100t/h
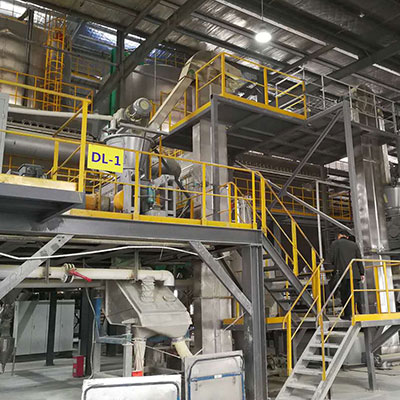 LiFePO4 Lithium Iron
LiFePO4 Lithium Iron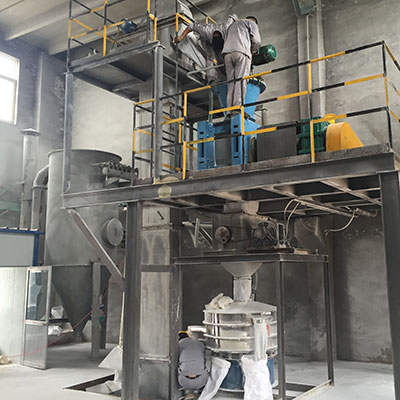  Snowmelt Salt
Snowmelt Salt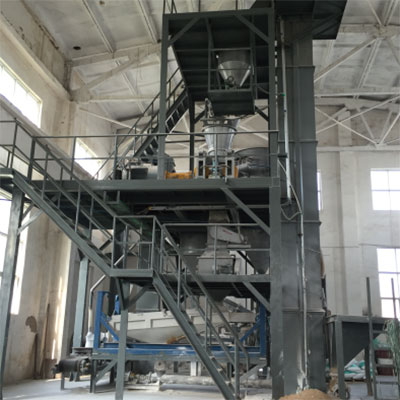  KCl Sodium Chloride
KCl Sodium Chloride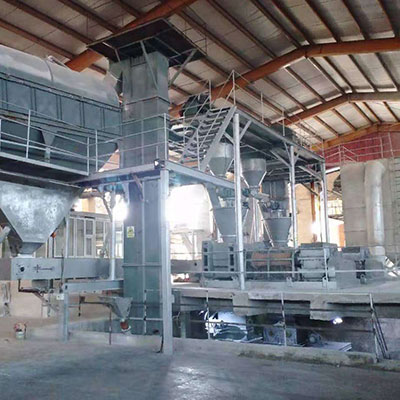  SOP Potassium Sulfate
SOP Potassium Sulfate 





What is Cyanuric Acid and Its Applications Cyanuric acid (CYA) is an…

What is Potassium Sulfate and Why Granulate It Potassium sulfate, commonly referred…

With the rise of precision agriculture and crop-specific nutrient strategies, specialty compound…

In briquetting, the binder is often the unsung hero. Whether you’re compacting…

Mixing and pelletizing processes are very important steps in the sintering production…

The Main Source of Ammonium Chloride The combined Alkali process (Hou’s process)…