What is sponge iron
Sponge iron, also known as DRI (direct reduced iron or direct reduction iron), bulk density 1.6-1.9g/cm3, apparent density 3.4-3.6g/cm3, typical size 4-20mm, is a kind of material produced by the reduction of iron ore with reducing gases such as H2 or CO gas generated from various carbon or hydrocarbon resources. The name is got because iron ore is reduced to form a large number of pores, which looks like a sponge under the microscope. In addition to the metallic iron content sponge iron contains some unreduced iron oxides and gangue. Since there is no separation of impurities in direct reduction process, all the gangue present in the original oxide (silica, alumina, oxides of phosphorous) goes into the product sponge iron.

How to produce sponge iron from iron ore
Sponge iron is obtained by reducing iron concentrate with hydrogen or other reducing gases. Generally, the iron ore is loaded into the reactor, and hydrogen, CO gas or solid reducing agent is used to react in a temperature range lower than the softening point of the iron ore, and neither molten iron nor slag will be generated. Only the oxygen in the iron oxide is removed to obtain porous metallic iron, that is, sponge iron.
There are many direct reduction methods, such as packed bed process (HYL), shaft furnace method (typical: Midrex), rotary kiln method (typical: SL/RN) and rotary hearth furnace (typical: fastmet) etc. There are more than 40 kinds of processes have been used for sponge iron making. But until now, more than 50% of the DRI produced in the steel plant is following the Midrex process.
The Midrex sponge iron plant process
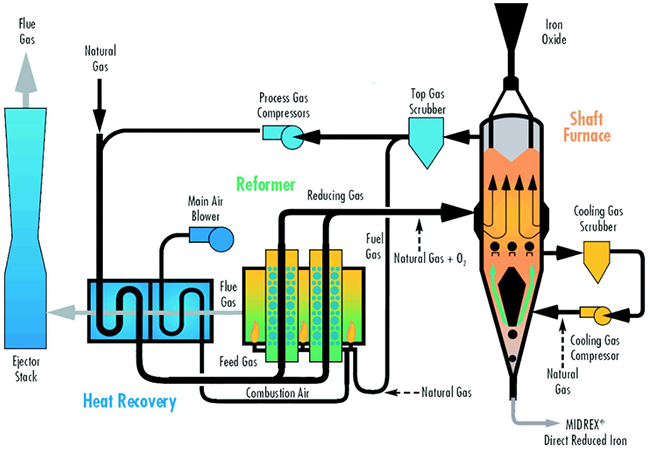
The Midrex DRI making process is a typical process for shaft furnaces. The main equipment are: shaft furnace, reformer and heat recovery. The reduction in the shaft furnace is carried out continuously. The oxidized and roasted pellets are loaded from the top of the furnace, move downward by their own weight, and the DRI is discharged from the bottom.
There are actually two independent process zones inside the shaft furnace, both of which use their own independent circulating gas. In the upper process zone, the pellets are preheated and reduced (approximately 1000°C) by a reducing gas containing H and CO. In the lower process zone, the reduced metallized pellets are carburized by a cold reducing gas and cooled ( close to below 550°C) until unloading.
Natural gas is used as the main reducing agent source. In practical production, the mixed gas for furnace reduction is composed of new natural gas and circulating gas returned from the top of the shaft furnace.
The Midrex reformer is a gas-sealed shaft furnace lined with refractory bricks and containing alloy tubes filled with catalyst. The mixture preheated by heat recovery flows upward through the catalyst layer, reforming and reheating at the same time. The hot reducing gas leaving the reformer is immediately sent to the reduction zone of the shaft furnace to reduce iron oxides.
The Midrex process has greatly improved the heat utilization rate due to the sensible heat network collection device. The heat recovery device includes the gas channel in the reformer and the heat recovery with a tubular structure. In this way, the sensible heat brought out by the reduction process gas is used to preheat the combustion air (that is, the reformer burner, which can be preheated to 675°C) and the furnace charge gas (the mixture gas sent to the reformer pipeline, which can be Preheating to 540°C), the heat recovery device reduces the heat consumption of the process (unit: ton) from greater than 14. 63GJ in 1969 to the present 9. 85GJ.
The iron-containing raw materials used in this method can be pure lump ore or pellets, or both can be used together in any proportion. The production capacity of the equipment is much larger than that of the packed bed process because of its continuous production, and it is easy to realize the automatic control of the reduction process.
Why make sponge iron briquette
During handling or transport of the reduced sponge iron pellets, there are attrition and abrasion of the hard and rough pellets that generate fines. There is difficulty in the handling of such fines. It can be used as a part of sinter additives or more readily as iron-bearing materials in the basic oxygen furnace or electric arc furnace.
The fine DRI produced by the fluidization method without passivation treatment cannot be stored in the open air, and the open-air storage of metallized sponge iron pellets is also very difficult. Stacking in small piles is beneficial to evacuate the heat released by the oxidation reaction and can inhibit spontaneous combustion. However, storage in large piles can reduce surface exposure and effectively reduce re-oxidation. Therefore, storage in large piles should be adopted under the condition of ensuring that spontaneous combustion does not occur.
The ideal storage method for DRI is to store it in a clean and waterproof airtight silo. When transporting DRI over a long distance by land or sea, it is best to process DRI first with passivation briquetting, and for fine powder products produced by fluidization method, passivation briquetting must be carried out first.
The benefit of using sponge iron briquette in steel making
In steel mills, sponge iron can be used in converters, electric furnaces and BOF as raw materials for steelmaking. Aalso can be used in blast furnace charges to increase metallization rate of raw material and as raw materials for powder metallurgy, but most of the sponge iron and sponge Iron briquette are used in the process of electric furnace steelmaking.
In the electric furnace steelmaking process, sponge iron has many advantages compared with scrap steel and pig iron due to its low carbon content (normally less than .05%), stable chemical composition, and low content of harmful elements.

Sponge iron briquette can be used as a coolant in the converter process and as a diluent in special steel smelting
- The bulk density of briquette is higher than that of slag in steelmaking, and it can penetrate the slag layer and enter below the slag surface, which can not only melt quickly, but also prevent secondary oxidation. If the sponge iron briquette is of high quality (first grade), The recovery rate of molten steel can reach more than 85%, generally speaking, the minimum recovery rate of molten steel can be higher than 80%.
- Sponge iron briquette has low carbon content, which is very beneficial when used as a coolant in the converter process, and has little effect on the carbon content in molten steel, which can shorten the smelting cycle and increase daily output;
- The chemical composition of sponge iron briquette is stable, and the content of harmful elements is low. This is the unique quality of sponge iron. When smelting high-quality steel or special steel, only adding sponge iron or high-quality steel scrap can guarantee the chemical index requirements of molten steel. High-quality steel scrap may have uneven quality and inclusions, so sponge iron briquette is the first choice.
- Sponge iron briquette also contains a small amount of iron oxides without reduction, which is beneficial to decarburization in the later stage of molten steel smelting.
- The single block of sponge iron briquette is small in weight and easy to use.
Sponge iron VS Steel scrap
- Steel scrap has many non-metallic inclusions, high content of harmful elements, and uneven quality. The sponge iron briquette is very pure.
- Although the bulk density of steel scrap is higher than sponge iron briquette, it is no problem for sponge iron briquette to penetrate the slag layer. If using high-quality sponge iron briquette, there is no difference in the yield of molten steel compared with scrap steel.
- Steel scrap needs to be cut, sponge iron briquette does not need to be cut.
- Depending on the quality and addition amount of steel scrap, the smelting cycle is lengthened, because there are many non-metallic inclusions, and the smelting time needs to be increased when the content of harmful elements and main elements is high. The sponge iron briquette is very pure, and there is no need to increase the smelting time after adding it.
Sponge Iron VS Pig Iron
- The carbon content of pig iron is high, generally around 4%. When it is used as a coolant in the converter process, it has a great impact on the carbon content of molten steel. Repeated blowing is required, which prolongs the smelting time. However, the carbon content of sponge iron briquette is low, which has little effect on the carbon content of molten steel, and can shorten the smelting time.
- The content of harmful elements such as S and P in pig iron is high, and the addition in the later stage of smelting has a great impact on the chemical composition of molten steel, while sponge iron briquette is very pure, which avoids this problem.
- The market price of pig iron is relatively high, while the price of sponge iron briquette is relatively low.
How to use sponge iron briquette in electric arc furnace (EAF)
- The application field of sponge iron briquette is mainly to smelt special steel in electric furnace instead of high-quality scrap steel as smelting raw material or as diluent. It is used as coolant in converter process.
- When replacing high-quality steel scrap as smelting raw material, the acid oxide content must be considered. If the acid oxide content is too high (for example, silicon dioxide is higher than 5%), the amount of slag should be considered. When the silicon dioxide is high, it should be mixed with steel scrap. Add or use as a diluent, adjust the dosage in time according to the level of silica.
- When used as a coolant in the converter process, due to the high content of acidic oxides, the amount of active limestone to be added should be calculated before adding. The two materials should be added together, which can effectively avoid the reversion problem caused by the change of slag basicity in the molten pool, also can shorten the smelting time.
- When a large amount of sponge iron briquette is used in the electric furnace, a certain amount of molten steel should be left at the bottom of the furnace to facilitate accelerated melting.
Sponge iron briquette machine
Sponge iron fine briquette machine mainly refers to the roll briquette machine. Due to the characteristics of sponge iron, as well as the quality requirements of the finished product, the required pressure is relatively high in the roll briquetting of common materials.
The fine mixture (DRI along with binder) is fed into the gap between two rolls rotating toward each other, on the surface of which symmetrically located cells in the form of semi-briquettes are arranged in a checkerboard pattern. During the rotation of the rolls, there is a convergence of cells, the capture of the material, and its sealing compression. The briquetted material is subjected to bilateral compression, which contributes to a more uniform distribution of its density by volume. Then, as the rolls rotate, the cells diverge, and the DRI briquette drops out of the cell under its own gravity.
The sponge iron briquette (CBI) has some advantages over bulk sponge iron which include higher density, higher oxidation resistance, lower water absorption and flexible carbon content. These advantages not only make its storage and shipment easier and more economic but also, have significant effects on its steelmaking behavior.

Sponge iron briquette making process
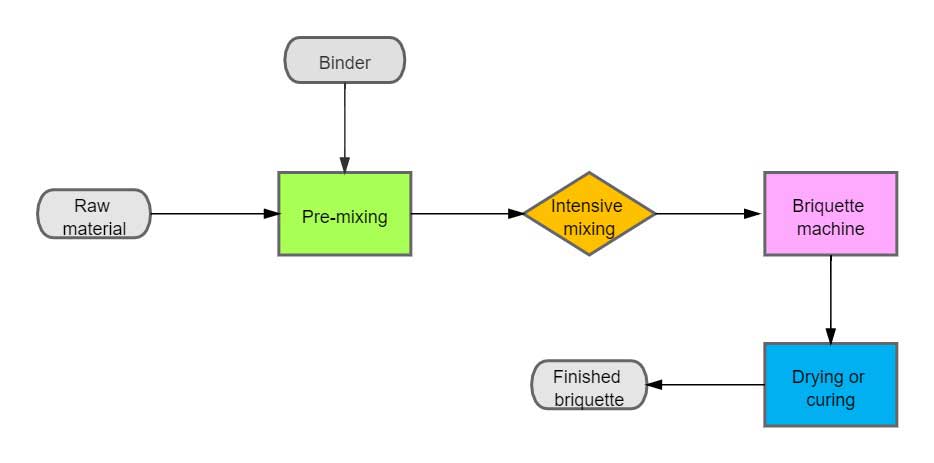
Cold sponge iron briquetting is a process of adding binders to agglomeration, similar to many binder briquetting materials, it is necessary to add appropriate additives to form during the briquetting process.
After the sponge iron is mixed with binder, it can enter the roller press for briquetting, and the briquetted sponge iron can be put into the furnace after being placed for a period of time. For the sponge iron briquette that needs to be sold, it is also feasible to pack and ship directly.
A simple sponge iron briquette making system will include dosing system, mixing system, and briquetting system.
In addition to providing a complete set of briquetting processes, Maxton can also provide various types of equipment customized according to customer needs, feeding and discharging systems, and docking with on-site raw material systems as well as dust removal systems, or a complete set of EPC systems and corresponding solutions.
The hot sponge iron briquetting
Hot sponge iron briquette, also known as HBI, is in the form of pellets, lumps, fines at a temperature of 650-700 Celsius is passed through hot roll briquetting machine where the product is pressed between the rolls at extremely high pressure to produce highly compacted pillow shaped material called hot briquetted iron.

A HBI production plant typically includes of the following sections:
- HBI Briquetting press with screw feeder and material supply
- Briquette string separator
- Hot screen for the elimination of fines which occur during briquetting and separation
- Product cooler
- Bucket elevator for the recirculation of hot fines to the briquetting press
- Chutes and accessories
Price of a sponge iron briquette system
There are not many equipments in the sponge iron (DRI) briquetting system. A simple process would include dosing machine, mixing machine and briquetting machine. However, according to customer’s requirements, operating habits and raw material conditions, the configuration of various equipment can be very different. Therefore, the specific price depends on many aspects. Only when you really understand the demand can we find out the corresponding price.
Cost for a hot briquette system would be quite much different from the CBI making system.





