







Rotary drum dryer also known as tumbling dryer is a drying equipment employed to minimize the moisture content of a feed material by bringing it into a slightly tilted and rotated drum where heat transfer happens and reduces the moisture.
The tumble dryer is one of the oldest drying equipment.
The wet material enters the drum from the feeding device and exchanges heat with the drying medium in the drum (mainly in the way of conduction and convection). The drum is normally equipped with lifting plates to make the material fall after being picked up. During the drying process, due to the action of gravity, the material will move from the higher end to the lower end of the drum, and finally reach the lower part of the other end and output from there.
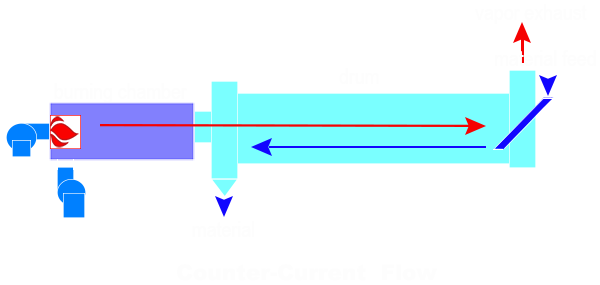
According to the flow direction of materials and hot air, the drum dryer can be divided into two drying methods: co-curnter flow and counterflow.
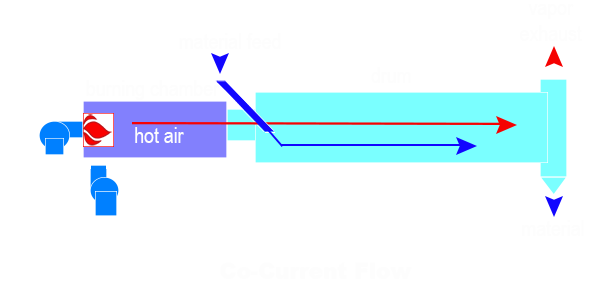
Co-current flow rotary drum dryers are the most widely used and are particularly suitable for drying materials containing a high moisture content. Due to the large temperature difference between the raw material and the hot air, the heat transfer speed is fast at the beginning, the heat transferred to the material is large, and the rapid drying is rapid, so the evaporation of water is also large. As the material and the flue gas continue to move, the moisture in the material decreases, the temperature rises, the water content in the flue gas increases, the temperature decreases, the temperature difference between the two gradually decreases, the heat transfer per unit time is gradually reduced, and the residual moisture contained in the material reaches the discharge end. This dryer is suitable for drying materials with high initial moisture and technical requirements for drying temperature.
Examples: filter cakes, minerals, fertilisers, beet pulp, de-greased bone, floatation concentrates, coal/coke, clays, phosphates, animal feeds, germ, stillage, sludges.
Counterflow rotary drum dryer is characterized by the opposite direction of the flow of the material in the cylinder to the flue gas. At the feeding end (the high end of the dum), the wet material with a lot of moisture and low temperature meets the flue gas with a lot of moisture and a low temperature that is about to be discharged into the dryer. At the discharge end (the low end of the drum), the dried material that has been dried and the temperature has risen is in contact with the hot flue gas of the dryer that has just entered the dryer. Therefore, the temperature difference between the material and the flue gas at each point in the whole cylinder is relatively uniform, and the heat transfer efficiency is relatively high. In the drying process, the drying speed is more uniform, and the heat and mass transfer are more balanced, avoiding the situation of hard drying surface. Compared with the co-current flow type, the drying time is longer, and the residual moisture of the material is small. It is suitable for drying materials with too much moisture at the input and less residual moisture.
Examples: silica gel, sugar, chemical salts and crystalline products (low temperature range) ammonium nitrate, ores and minerals, pigments, removal of floatation reagents.
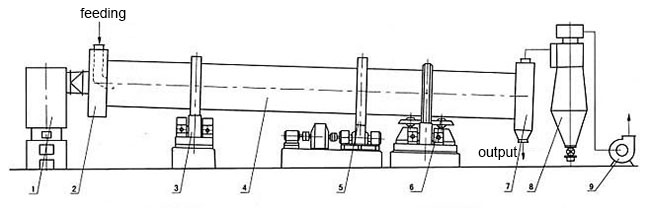
1. Heat system 2. Feeding device 3. Riding ring 4. Drum 5. Transmission device 6. Sprocket guard 7. Output device 8. Dust collector 9. ID Fan
The hot air is normally supplied as products of combustion from an oil, gas or solid fuel (pellet, coal, etc.) fired furnace in the temperature range 250ºC to 1000ºC as required for directly contact material.
Normal material carbon steel, varies optional material choices like manganese steel, stainless steel, etc.
Inner cross installed with shoveling plate, chain or lifting paddles, etc. to improve the drying efficiency for different materials.
The drum head and tail assemblies interface seal with the rotating drum incorporates an elastic wear resistant steel sheet providing long service life while being easy to assemble and maintain.
Drum driving gear ring and gear wheel arrangement is characterized by heavy duty cast and machined components ensuring optimum strength, stable operation, high resistance to wear and long service life
The choice of dust collection equipment will vary according to the application, but in addition to the range of high efficiency and high capacity cyclones, a bag filter, wet scrubber or scrubber/condenser can be supplied as required.
Drum dryer takes viscous liquids, slurries, suspensions, and pastes as input material to be dried and produces the output as powders or flakes. Drum dryers find application majorly in Metallurgy, Building materials, Food & Dairy industry , Chemical & Pharmaceutical Industries for drying various type of pasts and slurries.
• Minerals like iron ore, bauxite, copper ore, etc.
• Ore concentrates
• Bentonite
• Sludge
• Clay
• Coal
• Coke
• Bark
• Sawdust
• Sand
• Rubber Pellet
• Salt
• Sugar
• Fertilizer
• PVC
• Chicken Beef Feces
• Cassava Dregs
• Starch Residue and Sauce Residue
• Grass
• Straw
• Cereal Based Baby Foods
• Milk For Milk Powder
• Skim Milk
• Tomato Puree
• Broth
• Yeast
• Coffee Powder
• Malt Extract
• Apple Puree
• Apple Sauce
• Rice
• Wheat
• Maize
• Sauces And Jams
• Corn
• Soybean
• Banana
• Cowpea
• Citrus Pulps
• Fruit Juice
• Calcium Carbonate
• Suspension Of Zinc Oxide
• Sodium Benzoate
• Brewer’s Yeast
• Calcium Chaloride
• Potasium Phenyl Acetate
• Polycrylamide Gel
• Sodium Acetate
• Dye Intermediate
• Sulphur Black
• Calcium Lactate
• Antibiotics
• Insecticides
• Resis Salt
• Ammonium Sulfate
• Ammonium Nitrate
• Compound Fertilizer
The single pass drum is built with full length, flighting fixed to the interior of the drum. As the drum rotates at a constant speed, the positioned lighting continuously lifts and product up and drops it from through the heated air. The drying process occurs while the product is in suspension. Once product moisture is removed, the material is conveyed to the collecting place.
Characteristics
The triple pass drum consists of two concentric cylinders within one large outer cylinder. These fixed cylinders are aligned to rotate at the same speed. The inner cylinder maintains the highest temperature with progressively lower temperatures and air velocities in the intermediate and outer cylinders. The suction fan draws the material through the inner cylinder, back through the intermediate cylinder and then forward through the outer cylinder into the discharge end of the drum. The product is carried to the top of each cylinder by built-in flights.
Characteristics
directly fired, indirectly fired






When using a rotary dryer in potash fertilizer production, several efficiency-related issues may arise. Based on practical experience and systematic…
Read More »
Why drying coal sludge Coal sludge generally refers to a semi-solid substance formed by coal powder with water. It is…
Read More »
What is a rotary dryer The main body of the rotary dryer is a slightly inclined (or sometimes horizontal) rotating…
Read More »
When using a rotary dryer in potash fertilizer production, several efficiency-related issues…

Why drying coal sludge Coal sludge generally refers to a semi-solid substance…

What is a rotary dryer The main body of the rotary dryer…