What is water softnter salt briquette
Water softener salt briquette, also known as ion exchange resin regenerants, primarily consist of sodium chloride with a content exceeding 99%.
It is typically briquetted into pillow or square shape using a roller salt briquette machine. The briquette is mainly used in high-end water softening systems to provide a high concentration of sodium ions for the regeneration of ion exchange resins. Paired with water softeners, they efficiently remove water hardness (calcium, magnesium ions, and other impurities) to make the water cleaner and clearer, ensuring that water supply pipes remain unobstructed and free of scale.
The use of water softener salt leaves no residue or odor and outperforms other regenerants under the same conditions. It is suitable for all types of water softeners. Due to its non-toxic, harmless, low-cost, and high regeneration efficiency characteristics, it is widely used in boilers and household water softening equipment, with a broad market prospect.
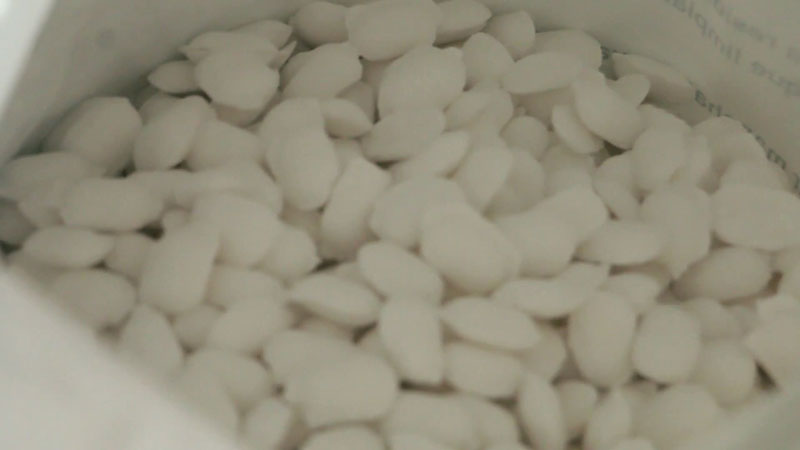

Which Salts Are Used in Ion Exchange Water Filters
Ion exchange water softeners utilize salts, mainly sodium chloride and potassium chloride to provide the soft ions that replace the hardness ions. The salt solution or brine is essentially held in the brine tank and is periodically flushed through the resin beads to regenerate them. Over time, the salt in your brine tank will deplete forcing you to restock by buying salt pellets, crystals, or blocks from local shops. Here are the primary salts that you are likely to find:
Evaporated salt (PDV salt)
Of all the water softening salts, evaporated salts are the purest hence they are relatively expensive. Their high purity levels (99.6 to 99.99%) mean that they are very soluble in water and the chances of mushing occurring are very limited. They are mainly sourced from underground salt reservoirs.
Rock salt
Rock salt is primarily found in the form of pebbles or small rocks. It is mined using conventional mining technologies from underground reservoirs and contains relatively high concentrations of calcium sulfate. This gives it an insolubility score of 0.5-1.5%, which can cause mushing. The concentration of sodium chloride in rock salt is approximately 98 to 99%.
Disadvantages of Using Unqualified Water Softener Salt Briquettes
The quality of the briquette is important for the salt tank. When the salt briquettes disintegrate in the salt tank, they can block the tank’s outlet, hindering the ion exchange resin regeneration process. This directly affects the normal operation of the water softener and, in severe cases, can damage the equipment, leading to unnecessary losses.
9 Factors Affecting the Quality of Water Softener Salt Briquettes
1. Raw Material
The primary raw material for water softener salt is refined edible salt. The purity, indicated by the sodium chloride content, is crucial. Higher sodium chloride content theoretically provides more sodium ions during the softener’s backwash, leading to more thorough resin regeneration and better water quality. According to Chinaese national standard GB/T 5461, the sodium chloride content in top-grade refined salt should be ≥99.1%.
EU standard: BS EN 973: 2009, Chemicals used for treatment of water intended for human consumption. Sodium chloride for regeneration of ion exchangers.

2. Moisture
During the production of water softener salt from refined edible salt, excessive moisture in the raw material can affect the flow speed of the material in the machine, leading to inadequate filling and insufficient compactness of the salt briquettes. This makes them prone to collapse and block the salt inlet. According to GB/T 5461, the water-insoluble content in top-grade refined salt should be ≤0.30 g/100 g.
3. Water Insoluble Substances
Water insoluble substances are key indicators of salt hygiene quality. They include mechanical impurities like sand, wood chips, suspended matter, and insoluble residues like calcium and magnesium carbonates and organic residues. High levels of insoluble substances affect the sodium chloride content and can contaminate ion exchange resins during backwashing, reducing their capacity and causing “resin poisoning”. According to GB/T 5461, the water-insoluble content should be ≤0.03 g/100 g.
4. Metal Elements (Except Sodium)
Metal elements in raw salt include iron, calcium, magnesium, potassium, barium, aluminum, lead, cadmium, tin, nickel, and chromium. Elements like lead, cadmium, tin, nickel, and chromium are regulated as food contaminants under GB 2762-2017. High-valence metal ions such as Al3+ and Fe3+ can enter the ion exchange resin, bind strongly with fixed ions, and reduce ion exchange capacity, causing “resin poisoning”.
5. Production
Production equipment, including roller briquette machines, powder feeders, conveyors, and weighing scales, significantly affects the quality of water softener salt briquette. Insufficient pressure or excessive roller speed can lead to inadequate compactness. Contamination during cleaning and maintenance can also affect quality. Proper machine maintenance and optimized production processes are essential.
6. Workshop Environment
Humidity and dust in the workshop affect the quality of water softener salt. High humidity can cause the raw salt to absorb moisture, leading to inadequate filling and poor compactness. Generally, humidity should be controlled between 30% and 60%. Dust affects the equipment and workers, indirectly impacting salt quality.

7. Finished Product Testing
Finished product testing involves checking the integrity, color, density, hardness, dissolution rate, and the amount of fine salt in the packaged product. Excessive fine salt can block the salt inlet.
8. Transportation
Transport can cause salt briquettes to break due to handling, vehicle bumps, and unclean vehicles. This increases fine salt content and potential contamination.
9. Storage
Storage environments must be ventilated, cool, and dry. High humidity can cause salt briquettes to absorb moisture and collapse. Proper storage ensures product quality.
Ways to Improve the Quality
Raw Material Improvement
Strict control over the raw material’s physical and chemical properties, especially purity, moisture, insoluble substances, and metal ion content. Choose sodium chloride that meets or exceeds standards.

Production Process Optimization
Upgrade production equipment to maintain proper pressure and speed. Regular maintenance and replacement of parts are crucial. Control workshop temperature and humidity, ensure a clean environment, and increase quality checks. Optimize handling and storage conditions.
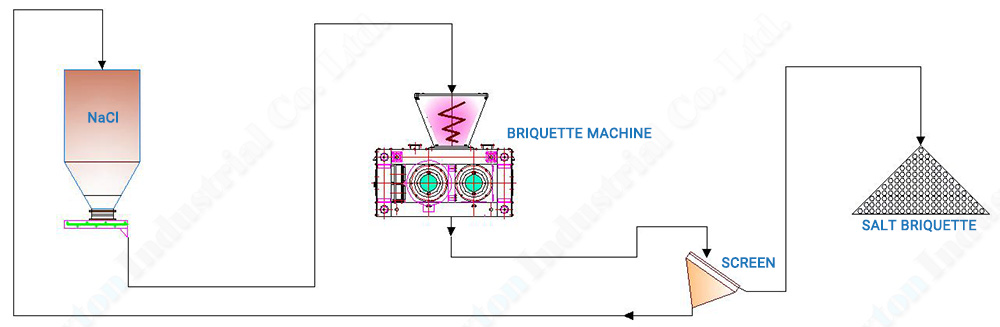
The production process of making water softner salt briquette
The process consists in briquetting under pressure sodium chloride into briquette.
Generally, salt is agglomerated after the drying step which reduces the moisture to less than 0,2%. A force feeder or a gravity feeder feeds the salt between two rotating parallel rollers turning in opposite directions. This process allows the formation of briquettes.
The quality of salt determines the compression roller speed and the pressure level.
Additionally, the size range has a great influence on the choice of feeding systems in presses (gravity or force feeder).
Find more for salt briquetting





